서비스 메시란?

- 클라우드에서 마이크로서비스를 운영하는 데는 여러 도전과제가 있다. -> 몇 가지를 꼽자면 신뢰할 수 없는 네트워크, 서비스 가용성, 이해하기 어려운 트래픽 흐름, 트래픽 암호화, 애플리케이션 상태, 성능 등이 있다.
- 이런 어려움들은 각 애플리케이션 내에서 라이브러리를 사용해 패턴(서비스 디스커버리 등)들을 구현함으로써 완화된다.
- 서비스들에 대한 관찰 가능성을 확보할 목적으로 메트릭과 트레이싱을 생성하고 배포하려면 추가적인 라이브러리와 서비스가 필요한다.
- 서비스 메시는 이런 공통 관심사(애플리케이션 네트워킹)를 애플리케이션 대신 외부에서 투명한 방식으로 구현하는 인프라
기본 동작 : 파드 간 통신 경로에 프록시를 놓고 트래픽 모니터링이나 트래픽 컨트롤 → 기존 애플리케이션 코드에 수정 없이 구성 가능!



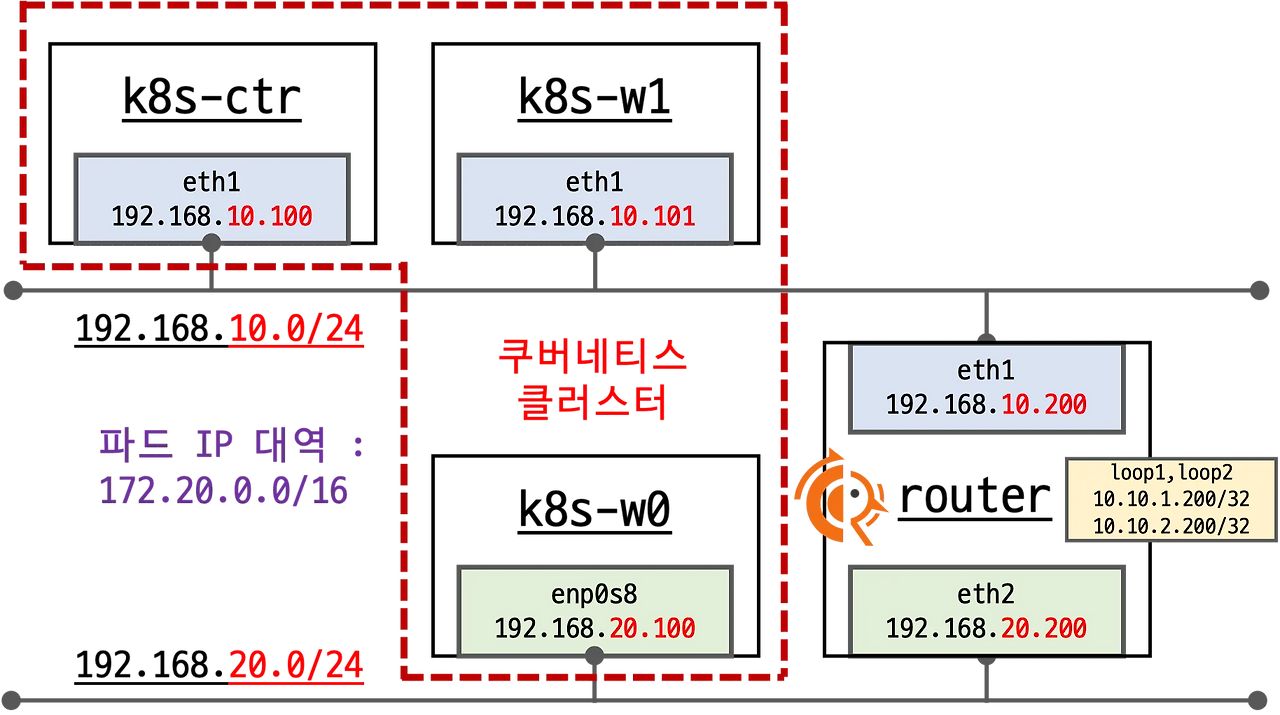
실습 환경 소개 :
- 실습 환경 소개 : k8s(1.33.4), cilium(1.18.1), pwru
- 기본 배포 가상 머신 : k8s-ctr, k8s-w1, router
- k8s-ctr spec : vCPU 4, Mem 2560
- k8s-w spec : vCPU 4, Mem 2560
- router : 192.168.10.0/24 ↔ 192.168.20.0/24 대역 라우팅 역할, k8s 에 join 되지 않은 서버
- 실습 동작에 필요한 static routing 설정 됨 with vagrant script file
- 기본 배포 가상 머신 : k8s-ctr, k8s-w1, router
1. 샘플 애플리케이션 배포 및 통신 문제 확인
# 샘플 애플리케이션 배포
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: webpod
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: webpod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: webpod
spec:
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app
operator: In
values:
- sample-app
topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
containers:
- name: webpod
image: traefik/whoami
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: webpod
labels:
app: webpod
spec:
selector:
app: webpod
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: ClusterIP
EOF
# k8s-ctr 노드에 curl-pod 파드 배포
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: curl-pod
labels:
app: curl
spec:
nodeName: k8s-ctr
containers:
- name: curl
image: nicolaka/netshoot
command: ["tail"]
args: ["-f", "/dev/null"]
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
EOF2. 통신 문제 확인
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl exec -it curl-pod -- sh -c 'while true; do curl -s --connect-timeout 1 webpod | grep Hostname; echo "---" ; sleep 1; done'
Hostname: webpod-697b545f57-r2jnp
---
Hostname: webpod-697b545f57-bbtvx
---
Hostname: webpod-697b545f57-r2jnp
---
Hostname: webpod-697b545f57-bbtvx
---
Hostname: webpod-697b545f57-r2jnp
---
Hostname: webpod-697b545f57-bbtvx
---
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl exec -it curl-pod -- curl -s --connect-timeout 1 webpod | grep Hostname
Hostname: webpod-697b545f57-bbtvx- Why Cilium Service Mesh?
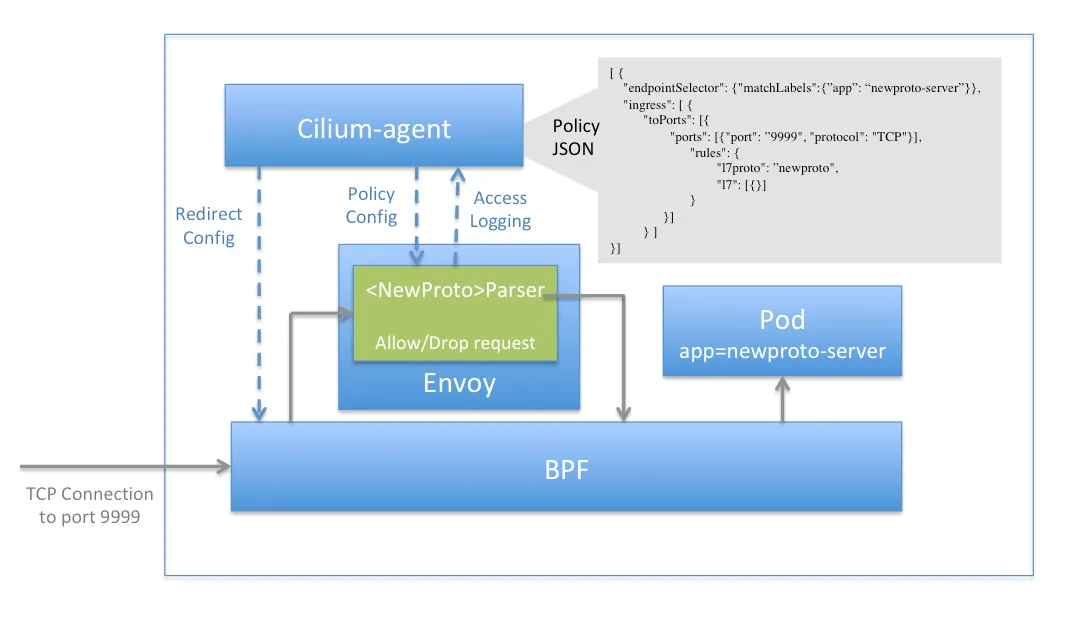
- L3/L4 수준 프로토콜 : eBPF 처리
- IP, TCP, UDP와 같은 프로토콜을 포함한 모든 네트워크 처리에 대해 Cilium은 고효율 커널 내부 데이터 경로로 eBPF를 사용.
- For all network processing including protocols such as IP, TCP, and UDP, Cilium uses eBPF as the highly efficient in-kernel datapath
- L3/L4 수준 프로토콜 : eBPF 처리



- L7 수준 애플리케이션 : cilium-envoy 처리
- HTTP, Kafka, gRPC, DNS와 같은 애플리케이션 계층 프로토콜은 Envoy와 같은 프록시를 사용하여 파싱.
- Protocols at the application layer such as HTTP, Kafka, gRPC, and DNS are parsed using a proxy such as Envoy.
Cilium uses the standard Kubernetes Ingress resource definition, with an ingressClassName of cilium.

- This can be used for path-based routing and for TLS termination. For backwards compatibility, he kubernetes.io/ingress.class annotation with value of cilium is also supported.
- The ingress controller creates a Service of LoadBalancer type, so your environment will need to support this.
- Cilium allows you to specify load balancer mode for the Ingress resource:
- dedicated: The Ingress controller will create a dedicated loadbalancer for the Ingress.
- shared: The Ingress controller will use a shared loadbalancer for all Ingress resources.
- Each load balancer mode has its own benefits and drawbacks. The shared mode saves resources by sharing a single LoadBalancer config across all Ingress resources in the cluster, while the dedicated mode can help to avoid potential conflicts (e.g. path prefix) between resources.
- It is possible to change the load balancer mode for an Ingress resource.
- When the mode is changed, active connections to backends of the Ingress may be terminated during the reconfiguration due to a new load balancer IP address being assigned to the Ingress resource. → 기존 모드 변경 시 LB IP 변경되어 Ingress 백엔드 활성 연결 종료됨.
🚀 실리움 envoy 확인
👉 cilium 설치 시 아래와 같이 파라미터 적용
# cilium 설치 시 아래 파라미터 적용되어 있음
## --set ingressController.enabled=true
## --set ingressController.loadbalancerMode=shared
## --set loadBalancer.l7.backend=envoy \
cilium config view | grep -E '^loadbalancer|l7'
enable-l7-proxy true
loadbalancer-l7 envoy
loadbalancer-l7-algorithm round_robin
loadbalancer-l7-ports
👉 cilium - envoy 별로 IP 를 할당 받음
# ingress 에 예약된 내부 IP 확인 : node(cilium-envoy) 별로 존재
kubectl exec -it -n kube-system ds/cilium -- cilium ip list | grep ingress
172.20.0.248/32 reserved:ingress
172.20.1.35/32 reserved:ingress
👉 cilium - envoy 확인
# cilium-envoy 확인
kubectl get ds -n kube-system cilium-envoy -owide
kubectl get pod -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium-envoy -owide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
cilium-envoy-6hc4t 1/1 Running 0 92m 192.168.10.100 k8s-ctr <none> <none>
cilium-envoy-cssvq 1/1 Running 0 90m 192.168.10.101 k8s-w1 <none> <none>👉 cilium - envoy 확인
kc describe pod -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium-envoy
...
Containers:
cilium-envoy:
Container ID: containerd://df0215f93e3193eaf81281e40cbdaa6ca1136c2ee3268fe3bcb60875f34bdbbf
Image: quay.io/cilium/cilium-envoy:v1.34.4-1754895458-68cffdfa568b6b226d70a7ef81fc65dda3b890bf@sha256:247e908700012f7ef56f75908f8c965215c26a27762f296068645eb55450bda2
Image ID: quay.io/cilium/cilium-envoy@sha256:247e908700012f7ef56f75908f8c965215c26a27762f296068645eb55450bda2
Port: 9964/TCP
Host Port: 9964/TCP
Command:
/usr/bin/cilium-envoy-starter
Args:
--
-c /var/run/cilium/envoy/bootstrap-config.json
--base-id 0
...
Mounts:
/sys/fs/bpf from bpf-maps (rw)
/var/run/cilium/envoy/ from envoy-config (ro)
/var/run/cilium/envoy/artifacts from envoy-artifacts (ro)
/var/run/cilium/envoy/sockets from envoy-sockets (rw)
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from kube-api-access-6gsbl (ro)
...
Volumes:
envoy-sockets:
Type: HostPath (bare host directory volume)
Path: /var/run/cilium/envoy/sockets
HostPathType: DirectoryOrCreate
envoy-artifacts:
Type: HostPath (bare host directory volume)
Path: /var/run/cilium/envoy/artifacts
HostPathType: DirectoryOrCreate
envoy-config:
Type: ConfigMap (a volume populated by a ConfigMap)
Name: cilium-envoy-config
Optional: false
bpf-maps:
Type: HostPath (bare host directory volume)
Path: /sys/fs/bpf
HostPathType: DirectoryOrCreate
#
ls -al /var/run/cilium/envoy/sockets
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 120 Aug 16 17:47 .
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 80 Aug 16 16:16 ..
srw-rw---- 1 root 1337 0 Aug 16 17:47 access_log.sock
srwxr-xr-x 1 root root 0 Aug 16 16:16 admin.sock
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 60 Aug 16 16:16 envoy
srw-rw---- 1 root 1337 0 Aug 16 17:47 xds.sock
#
kubectl exec -it -n kube-system ds/cilium-envoy -- ls -al /var/run/cilium/envoy
kubectl exec -it -n kube-system ds/cilium-envoy -- cat /var/run/cilium/envoy/bootstrap-config.json
kubectl exec -it -n kube-system ds/cilium-envoy -- cat /var/run/cilium/envoy/bootstrap-config.json > envoy.json
cat envoy.json | jq
# envoy configmap 설정 내용 확인
kubectl -n kube-system get configmap cilium-envoy-config
kubectl -n kube-system get configmap cilium-envoy-config -o json \
| jq -r '.data["bootstrap-config.json"]' \
| jq .
...
{
"admin": {
"address": {
"pipe": {
"path": "/var/run/cilium/envoy/sockets/admin.sock"
}
}
},
...
"listeners": [
{
"address": {
"socketAddress": {
"address": "0.0.0.0",
"portValue": 9964
...
tree /sys/fs/bpf
/sys/fs/bpf
├── cilium
│ ├── devices
│ │ ├── cilium_host
│ │ │ └── links
│ │ │ ├── cil_from_host
│ │ │ └── cil_to_host
│ │ ├── cilium_net
│ │ │ └── links
│ │ │ └── cil_to_host
│ │ ├── eth0
│ │ │ └── links
│ │ │ ├── cil_from_netdev
│ │ │ └── cil_to_netdev
│ │ └── eth1
│ │ └── links
│ │ ├── cil_from_netdev
│ │ └── cil_to_netdev
│ ├── endpoints
│ │ ├── 1059
│ │ │ └── links
│ │ │ └── cil_from_container
...(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get svc,ep -n kube-system cilium-envoy
Warning: v1 Endpoints is deprecated in v1.33+; use discovery.k8s.io/v1 EndpointSlice
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/cilium-envoy ClusterIP None <none> 9964/TCP 4h44m
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
endpoints/cilium-envoy 192.168.10.100:9964,192.168.10.101:9964 4h44m
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get svc,ep -n kube-system cilium-ingress
Warning: v1 Endpoints is deprecated in v1.33+; use discovery.k8s.io/v1 EndpointSlice
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/cilium-ingress LoadBalancer 10.96.69.146 <pending> 80:30162/TCP,443:31627/TCP 4h46m
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
endpoints/cilium-ingress 192.192.192.192:9999 4h46m
LB-IPAM 설정 후 확인 : CiliumL2AnnouncementPolicy
1. 현재 L2 Announcement ON
- lb ip pool 배포
# 현재 L2 Announcement 활성화 상태
cilium config view | grep l2
enable-l2-announcements true
enable-l2-neigh-discovery false
# 충돌나지 않는지 대역 확인 할 것!
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: "cilium.io/v2"
kind: CiliumLoadBalancerIPPool
metadata:
name: "cilium-lb-ippool"
spec:
blocks:
- start: "192.168.10.211"
stop: "192.168.10.215"
EOF
2. L2 Announcement 정책 설정 :
- external IPs : true
- LoadBalancer IPs: true
# L2 Announcement 정책 설정
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: "cilium.io/v2alpha1"
kind: CiliumL2AnnouncementPolicy
metadata:
name: policy1
spec:
interfaces:
- eth1
externalIPs: true
loadBalancerIPs: true
EOF
3. 내부, 외부 통신확인
- K8S 클러스터 내부 LB EX-IP로 호출 가능
- k8s 외부 노드(router)에서 LB EX-IP로 호출 가능 확인
# 현재 리더 역할 노드 확인
kubectl -n kube-system get lease | grep "cilium-l2announce"
kubectl -n kube-system get lease/cilium-l2announce-kube-system-cilium-ingress -o yaml | yq
# K8S 클러스터 내부 LB EX-IP로 호출 가능
LBIP=$(kubectl get svc -n kube-system cilium-ingress -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
echo $LBIP
arping -i eth1 $LBIP -c 2
# k8s 외부 노드(router)에서 LB EX-IP로 호출 가능 확인
LBIP=192.168.10.211
arping -i eth1 $LBIP -c 2

Ingress HTTP Example : XFF 확인
Ingress HTTP Example : XFF 확인
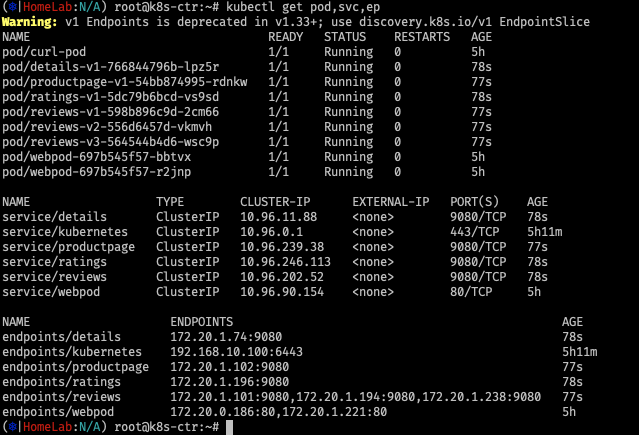
1. deploy demo app ( bookinfo)
# Deploy the Demo App : 공식 문서는 release-1.11 로 ARM CPU 에서 실패한다. 1.26 버전을 높여서 샘플 배포 할 것!
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.26/samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
# istio 와 다르게 사이드카 컨테이너가 없다 1/1 , NodePort와 LoadBalancer 서비스 없다.
kubectl get pod,svc,ep
2. ingress Class 배포
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: basic-ingress
namespace: default
spec:
ingressClassName: cilium
rules:
- http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: details
port:
number: 9080
path: /details
pathType: Prefix
- backend:
service:
name: productpage
port:
number: 9080
path: /
pathType: Prefix
EOF
3. 확인
- External IP가 세팅 됨 ( LB IP Setting )
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get svc -n kube-system cilium-ingress
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
cilium-ingress LoadBalancer 10.96.69.146 192.168.10.211 80:30162/TCP,443:31627/TCP 5h14m
4. 호출 확인
# 호출 확인
LBIP=$(kubectl get svc -n kube-system cilium-ingress -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
echo $LBIP
# 실패하는 호출이 있는가?
curl -so /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://$LBIP/
curl -so /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://$LBIP/details/1
curl -so /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://$LBIP/ratings
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -so /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://$LBIP/
200
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -so /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://$LBIP/details/1
200
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl -so /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://$LBIP/ratings
404
# Access the Bookinfo application
curl "http://$LBIP/productpage?u=normal"
5. hubble
# 모니터링
cilium hubble port-forward&
hubble observe -f -t l7
or
hubble observe -f --identity ingress
...
6. router에서 확인
root@router:~# curl -so /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://$LBIP/
200
root@router:~# curl -so /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://$LBIP/details/1
200
root@router:~# curl -s http://$LBIP/details/1 -v
* Trying 192.168.10.211:80...
* Connected to 192.168.10.211 (192.168.10.211) port 80
> GET /details/1 HTTP/1.1
> Host: 192.168.10.211
> User-Agent: curl/8.5.0
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< content-type: application/json
< server: envoy
< date: Wed, 20 Aug 2025 00:29:16 GMT
< content-length: 178
< x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 28
<
* Connection #0 to host 192.168.10.211 left intact
{"id":1,"author":"William Shakespeare","year":1595,"type":"paperback","pages":200,"publisher":"PublisherA","language":"English","ISBN-10":"1234567890","ISBN-13":"123-1234567890"}
7. w1 에 위치한 파드의 라우팅 테이블 확인
# productpage-v1 파드가 배포된 노드 확인
kubectl get pod -l app=productpage -owide
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get pod -l app=productpage -owide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
productpage-v1-54bb874995-rdnkw 1/1 Running 0 18h 172.20.1.102 k8s-w1 <none> <none>
# 해당 노드(k8s-w1)에서 veth 인터페이스 정보 확인
PROID=172.20.1.102
root@k8s-w1:~# PROID=172.20.1.102
root@k8s-w1:~# ip route |grep $PROID
172.20.1.102 dev lxcb75cf4d9b323 proto kernel scope link
8. ngrep
root@k8s-w1:~# ngrep -tW byline -d $PROVETH '' 'tcp port 9080'
lxcb75cf4d9b323: no IPv4 address assigned: Cannot assign requested address
interface: lxcb75cf4d9b323
filter: ( tcp port 9080 ) and ((ip || ip6) || (vlan && (ip || ip6)))
####
T 2025/08/20 09:35:14.972128 10.0.2.15:45812 -> 172.20.1.102:9080 [AP] #4
GET / HTTP/1.1.
host: 192.168.10.211.
user-agent: curl/8.5.0.
accept: */*.
x-forwarded-for: 192.168.10.200.
x-forwarded-proto: http.
x-envoy-internal: true.
x-request-id: f884b027-b3ba-4ffd-8e3d-133cdbf6ad87.
.
##
T 2025/08/20 09:35:14.980832 172.20.1.102:9080 -> 10.0.2.15:45812 [AP] #6
HTTP/1.1 200 OK.
Server: gunicorn.
Date: Wed, 20 Aug 2025 00:35:14 GMT.
Connection: keep-alive.
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8.
Content-Length: 2080.
.
##
T 2025/08/20 09:35:14.980899 172.20.1.102:9080 -> 10.0.2.15:45812 [AP] #8
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
9. envoy로 우회하는 트래픽
##
T 2025/08/20 09:35:14.980832 172.20.1.102:9080 -> 10.0.2.15:45812 [AP] #6
HTTP/1.1 200 OK.
Server: gunicorn.
Date: Wed, 20 Aug 2025 00:35:14 GMT.
Connection: keep-alive.
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8.
Content-Length: 2080.
.dedicated mode (독점 모드)
Cilium dedicated mode는 Cilium CNI가 Kubernetes 클러스터에서 네트워크 플러그인(CNI)으로만 동작하도록 제한된 실행 모드를 의미합니다.
보통 Cilium은 단순히 Pod 네트워킹만 담당하는 것이 아니라, eBPF 기반의 고급 기능(서비스 로드밸런싱, 네트워크 정책, 클러스터 간 연결, kube-proxy 대체 등)을 함께 제공합니다. 그런데 운영 환경에 따라 "Cilium을 다른 기능 없이 CNI로만 사용"해야 할 때가 있습니다. 이때 사용하는 설정이 바로 dedicated mode입니다.
주요 특징
- CNI 전용 모드
- Pod 네트워크 인터페이스 생성 및 라우팅만 담당
- kube-proxy 대체(kube-proxy replacement)나 kube-dns, API Server Proxy 같은 부가 기능은 비활성화
- IPAM 단순화
- 노드 단위에서 IP 할당만 담당
- 외부 IPAM 연동이나 고급 IP 관리 기능은 최소화 가능
- Deployment 단순화
- DaemonSet으로 배포되는 cilium-agent가 네트워킹만 수행
- cilium-operator 같은 일부 컨트롤 플레인 컴포넌트는 불필요할 수도 있음 (구성에 따라 다름)
- 사용 사례
- 기존에 kube-proxy, CoreDNS, Ingress Controller 등을 그대로 쓰고 싶을 때
- Cilium의 고급 기능(eBPF LB, Hubble observability 등)을 아직 도입하지 않고 싶을 때
- 네트워킹 안정성을 최우선으로 두고 단계적으로 Cilium 기능을 확장하려는 경우
# dedicated mode
# Basic ingress for istio bookinfo demo application, which can be found in below
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: webpod-ingress
namespace: default
annotations:
ingress.cilium.io/loadbalancer-mode: dedicated
spec:
ingressClassName: cilium
rules:
- http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: webpod
port:
number: 80
path: /
pathType: Prefix
EOF
#
kc describe ingress webpod-ingress
kubectl get ingress
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
basic-ingress cilium * 192.168.10.211 80 8m26s
webpod-ingress cilium * 192.168.10.213 80 8s
webpod-ingress-nginx nginx nginx.webpod.local 192.168.10.212 80 16m
kubectl get svc,ep cilium-ingress-webpod-ingress
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/cilium-ingress-webpod-ingress LoadBalancer 10.96.175.13 192.168.10.213 80:31067/TCP,443:30783/TCP 27s
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
endpoints/cilium-ingress-webpod-ingress 192.192.192.192:9999 27s
# LB EX-IP에 대한 L2 Announcement 의 Leader 노드 확인
kubectl get lease -n kube-system | grep ingress
# webpod 파드 IP 확인
kubectl get pod -l app=webpod -owide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
webpod-7d9dcd8859-7v76g 1/1 Running 0 16s 172.20.0.112 k8s-ctr <none> <none>
webpod-7d9dcd8859-kpjrj 1/1 Running 0 20s 172.20.1.38 k8s-w1 <none> <none>
# k8c-ctr, k8s-w1 노드에서 파드 IP에 veth 찾기(ip -c route) 이후 ngrep 로 각각 트래픽 캡쳐
WPODVETH=lxce95c39b2b4c4
ngrep -tW byline -d $WPODVETH '' 'tcp port 80'
# router 에서 호출 확인
LB2IP=$(kubectl get svc cilium-ingress-webpod-ingress -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
sshpass -p 'vagrant' ssh vagrant@router curl -s http://$LB2IP
Hostname: webpod-7d9dcd8859-kpjrj
IP: 127.0.0.1
IP: ::1
IP: 172.20.1.38 # webpod 파드 IP
IP: fe80::bce5:35ff:fee8:619e
RemoteAddr: 10.0.2.15:51984 # webpod 인입 시 S.IP : 마치 L2 Leader 노드에 webpod로 전달되어, 소스IP가 해당 노드의 첫 번째 NIC IP,
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: 192.168.10.212
User-Agent: curl/8.5.0
Accept: */*
X-Envoy-Internal: true
X-Forwarded-For: 192.168.10.200
X-Forwarded-Proto: http
X-Request-Id: 292040af-f112-4d04-9281-730da5a513d1
sshpass -p 'vagrant' ssh vagrant@router curl -s http://$LB2IP
Hostname: webpod-7d9dcd8859-7v76g
IP: 127.0.0.1
IP: ::1
IP: 172.20.0.112 # webpod 파드 IP
IP: fe80::607a:a1ff:fe34:205b
RemoteAddr: 172.20.1.35:46067 # webpod 인입 시 S.IP : L2 Leader 노드(k8s-w1)에서 다른 노드에 파드로 전달되어, ingress 예약IP로 SNAT
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: 192.168.10.212
User-Agent: curl/8.5.0
Accept: */*
X-Envoy-Internal: true
X-Forwarded-For: 192.168.10.200
X-Forwarded-Proto: http
X-Request-Id: dd65f484-8d20-4a4c-8eac-ed8666f64bdf✅ 정리하면, Cilium dedicated mode = Pod 네트워킹만 담당하는 최소 기능 모드입니다.
즉, 다른 네트워크 기능은 Kubernetes 기본 컴포넌트(kube-proxy 등)에 맡기고, Cilium은 순수 CNI 역할만 수행하는 형태라고 이해하시면 됩니다.
인그레스와 네트워크 폴리시
Ingress and Network Policy Example - Docs
CiliumNetworkPolicy(CNP)는 Cilium이 제공하는 Kubernetes 네트워크 정책 리소스로, Kubernetes 기본 NetworkPolicy보다 훨씬 강력한 기능을 제공합니다.
🔹 Cilium Network Policy란?
- Kubernetes NetworkPolicy는 L3/L4 (IP/포트) 수준의 통신 제어만 지원합니다.
- Cilium은 eBPF 기반으로 동작하기 때문에, 여기에 더해 L7 (애플리케이션 프로토콜) 수준까지 세밀하게 제어할 수 있습니다.
- CiliumNetworkPolicy(CNP)와 CiliumClusterwideNetworkPolicy(CCNP)를 CRD로 정의해서 사용합니다.
🔹 주요 특징
- L3/L4 제어 (IP, 포트 기반)
- 특정 Pod/Namespace/IP 블록과의 Ingress/Egress 허용
- TCP/UDP 포트 기반 제어
- L7 제어 (애플리케이션 프로토콜 인식)
- HTTP, gRPC, Kafka, DNS 등 프로토콜별 세부 정책 적용
- 예: HTTP Path, Method, Header 기반 접근 제어
- Kafka 토픽 단위 접근 제어도 가능
- 정책 범위
- CiliumNetworkPolicy: 네임스페이스 단위
- CiliumClusterwideNetworkPolicy: 클러스터 전역
- Identity 기반 제어
- Pod 라벨/네임스페이스 기반으로 동작
- IP 변화에 영향 받지 않음 → 오토스케일링 환경에 적합
- 정책 조합
- Kubernetes 기본 NetworkPolicy와 공존 가능
- Cilium 고유 정책(CNP/CCNP)만으로도 확장 가능
# 클러스터 전체(모든 네임스페이스)에 적용되는 정책 : 참고로 아래 정책 적용 후 Hubble-ui 로 접속 불가!
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: "cilium.io/v2"
kind: CiliumClusterwideNetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: "external-lockdown"
spec:
description: "Block all the traffic originating from outside of the cluster"
endpointSelector: {}
ingress:
- fromEntities:
- cluster
EOF
kubectl get ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicy
#
curl --fail -v http://"$LBIP"/details/1
< HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
#
hubble observe -f --identity ingress
## k8s-ctr 에서 curl 실행 시
Aug 16 14:02:01.011: 127.0.0.1:58328 (ingress) -> 127.0.0.1:14485 (world) http-request DROPPED (HTTP/1.1 GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1)
Aug 16 14:02:01.011: 127.0.0.1:58328 (ingress) <- 127.0.0.1:14485 (world) http-response FORWARDED (HTTP/1.1 403 0ms (GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1))
## router 에서 curl 실행 시
Aug 16 14:03:35.580: 192.168.10.200:56904 (ingress) -> kube-system/cilium-ingress:80 (world) http-request DROPPED (HTTP/1.1 GET http://192.168.10.211/)
Aug 16 14:03:35.580: 192.168.10.200:56904 (ingress) <- kube-system/cilium-ingress:80 (world) http-response FORWARDED (HTTP/1.1 403 0ms (GET http://192.168.10.211/))
# 스터디 시간(영상 녹화)에서 누락된 내용으로 아래 리소스 생성 후 진행하시면 됩니다!
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: "cilium.io/v2"
kind: CiliumClusterwideNetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: "allow-cidr"
spec:
description: "Allow all the traffic originating from a specific CIDR"
endpointSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: reserved:ingress
operator: Exists
ingress:
- fromCIDRSet:
# Please update the CIDR to match your environment
- cidr: 192.168.10.200/32
- cidr: 127.0.0.1/32
EOF
# 요청 성공! : k8s-ctr , router 모두 가능
curl --fail -v http://"$LBIP"/details/1
sshpass -p 'vagrant' ssh vagrant@router "curl -s --fail -v http://"$LBIP"/details/1"
# Default Deny Ingress Policy : DNS쿼리와 kube-system내의 파드 제외 to deny all traffic by default
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: cilium.io/v2
kind: CiliumClusterwideNetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: "default-deny"
spec:
description: "Block all the traffic (except DNS) by default"
egress:
- toEndpoints:
- matchLabels:
io.kubernetes.pod.namespace: kube-system
k8s-app: kube-dns
toPorts:
- ports:
- port: '53'
protocol: UDP
rules:
dns:
- matchPattern: '*'
endpointSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: io.kubernetes.pod.namespace
operator: NotIn
values:
- kube-system
EOF
kubectl get ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicy
# 요청
curl --fail -v http://"$LBIP"/details/1
sshpass -p 'vagrant' ssh vagrant@router "curl -s --fail -v http://"$LBIP"/details/1"
# ingress 를 통해서 인입 시 허용
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: cilium.io/v2
kind: CiliumClusterwideNetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-ingress-egress
spec:
description: "Allow all the egress traffic from reserved ingress identity to any endpoints in the cluster"
endpointSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: reserved:ingress
operator: Exists
egress:
- toEntities:
- cluster
EOF
kubectl get ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicy
#
curl --fail -v http://"$LBIP"/details/1
sshpass -p 'vagrant' ssh vagrant@router "curl -s --fail -v http://"$LBIP"/details/1"
# 정책 삭제
kubectl delete CiliumClusterwideNetworkPolicy --all(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# kubectl get ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicy
NAME VALID
external-lockdown True
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# curl --fail -v http://"$LBIP"/details/1
curl: (22) The requested URL returned error: 403
#클러스터 외주 요청 락다운 시킴
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# hubble observe -f --identity ingress
# ctr 요청
Aug 21 14:26:30.950: 127.0.0.1:47032 (ingress) -> 127.0.0.1:15930 (world) http-request DROPPED (HTTP/1.1 GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1)
Aug 21 14:26:30.950: 127.0.0.1:47032 (ingress) <- 127.0.0.1:15930 (world) http-response FORWARDED (HTTP/1.1 403 0ms (GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1))
# 라우터에서 요청
Aug 21 14:27:06.809: 192.168.10.200:49188 (ingress) -> kube-system/cilium-ingress:80 (world) http-request DROPPED (HTTP/1.1 GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1)
Aug 21 14:27:06.809: 192.168.10.200:49188 (ingress) <- kube-system/cilium-ingress:80 (world) http-response FORWARDED (HTTP/1.1 403 0ms (GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1))
# 정의된 CIDR의 모든 트레픽 허용
(⎈|HomeLab:N/A) root@k8s-ctr:~# hubble observe -f --identity ingress
# ctr 요청
Aug 21 14:30:11.109: 172.20.0.166:36991 (ingress) -> default/details-v1-766844796b-2mbl9:9080 (ID:29027) policy-verdict:L3-Only INGRESS ALLOWED (TCP Flags: SYN)
...
Aug 21 14:30:11.125: 127.0.0.1:59582 (ingress) <- default/details-v1-766844796b-2mbl9:9080 (ID:29027) http-response FORWARDED (HTTP/1.1 200 19ms (GET http://192.168.10.211/details/1))
# 라우터에서 요청
Aug 21 14:30:41.171: 172.20.0.166:36991 (ingress) <- default/details-v1-766844796b-2mbl9:9080 (ID:29027) to-network FORWARDED (TCP Flags: ACK, FIN)
Aug 21 14:30:41.172: 172.20.0.166:36991 (ingress) -> default/details-v1-766844796b-2mbl9:9080 (ID:29027) to-endpoint FORWARDED (TCP Flags: ACK, FIN)여기에서 주목할 점은 인그레스 엔드포인트를 대상으로 삼아 정책을 적용했다는 것이다.
앞선 정책에서 내부 통신은 전부 허용한 상태이기 때문에 인그레스에서 워크로드로 가는 트래픽 자체는 문제가 없었다.
그러므로 외부에서 인그레스로 들어가는 정책만 뚫어주면 통신이 가능해지는 것이다.
ingress path Type
인그레스 경로 유형
👍 Kubernetes Ingress에서 pathType은 Ingress 리소스가 정의한 경로(Path)를 어떻게 매칭할지 정하는 옵션입니다.
🔹 지원되는 Path Type
Kubernetes ≥1.18부터 세 가지 pathType이 있습니다.
1. Exact
- 요청 URL Path가 정확히 일치해야 매칭됩니다.
- /foo → /foo 만 허용
- /foo/ 나 /foo/bar 는 매칭 ❌
예시:
- path: /foo
pathType: Exact
backend:
service:
name: foo-service
port:
number: 80
2. Prefix
- 요청 URL Path가 지정한 경로로 시작하면 매칭됩니다.
- 경계는 / 단위로 구분
- /foo → /foo, /foo/, /foo/bar 매칭 ✅
- /foobar 는 매칭 ❌ (단어 경계 때문)
예시:
- path: /foo
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: foo-service
port:
number: 80
3. ImplementationSpecific
- 어떤 방식으로 Path를 해석할지는 Ingress Controller 구현체에 따라 다름
- 예: NGINX Ingress Controller는 regex-like 매칭을 허용할 수도 있고, 다른 컨트롤러는 단순 Prefix처럼 동작할 수도 있음.
- 이식성(portability)이 떨어지므로 권장되지 않음.
예시:
- path: /foo
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
backend:
service:
name: foo-service
port:
number: 80
아래 실습은 Cilium Ingress(ingressClass=cilium)가 pathType 별 매칭을 어떻게 처리하는지를 실제 트래픽으로 검증한 것입니다. 각 curl 결과가 가리키는 의미를 생각해보기
# Apply the base definitions
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/main/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/ingress-path-types.yaml
# 확인
kubectl get -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/main/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/ingress-path-types.yaml
# Apply the Ingress
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/main/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/ingress-path-types-ingress.yaml
# 확인
kc describe ingress multiple-path-types
kc get ingress multiple-path-types -o yaml
spec:
ingressClassName: cilium
rules:
- host: pathtypes.example.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: exactpath
port:
number: 80
path: /exact
pathType: Exact
- backend:
service:
name: prefixpath
port:
number: 80
path: /
pathType: Prefix
- backend:
service:
name: prefixpath2
port:
number: 80
path: /prefix
pathType: Prefix
- backend:
service:
name: implpath
port:
number: 80
path: /impl
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
- backend:
service:
name: implpath2
port:
number: 80
path: /impl.+
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
# 호출 확인
export PATHTYPE_IP=`k get ing multiple-path-types -o json | jq -r '.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip'`
curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/ | jq
# 파드명 이름 확인
kubectl get pod | grep path
exactpath-7488f8c6c6-pd4pc 1/1 Running 0 7m25s
implpath-7d8bf85676-f7k5s 1/1 Running 0 7m25s
implpath2-56c97c8556-mtnnm 1/1 Running 0 7m25s
prefixpath-5d6b989d4-w4qv2 1/1 Running 0 7m25s
prefixpath2-b7c7c9568-mkv8d 1/1 Running 0 7m25s
# Should show prefixpath
curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/ | grep -E 'path|pod'
"path": "/",
"host": "pathtypes.example.com",
"pod": "prefixpath-5d6b989d4-w4qv2"
# Should show exactpath
curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/exact | grep -E 'path|pod'
"path": "/exact",
"host": "pathtypes.example.com",
"pod": "exactpath-7488f8c6c6-pd4pc"
# Should show prefixpath2
curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/prefix | grep -E 'path|pod'
"path": "/prefix",
"host": "pathtypes.example.com",
"pod": "prefixpath2-b7c7c9568-mkv8d"
# Should show implpath
curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/impl | grep -E 'path|pod'
"path": "/impl",
"host": "pathtypes.example.com",
"pod": "implpath-7d8bf85676-f7k5s"
# Should show implpath2
curl -s -H "Host: pathtypes.example.com" http://$PATHTYPE_IP/implementation | grep -E 'path|pod'
"path": "/implementation",
"host": "pathtypes.example.com",
"pod": "implpath2-56c97c8556-mtnnm"
# 삭제
kubectl delete -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/main/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/ingress-path-types.yaml
kubectl delete -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/main/examples/kubernetes/servicemesh/ingress-path-types-ingress.yaml
- 기본 라우트는 / Prefix로 두고, 더 구체적인 경로는 별도 Prefix로 오버라이드한다.
- 특정 엔드포인트는 Exact를 써서 오탐 매칭을 방지한다.
- 컨트롤러 고유 동작이 필요한 경우(정규식 등) ImplementationSpecific를 사용한다. 이 경우 **이식성(다른 Ingress Controller로 교체 시 동작 차이)**은 낮아질 수 있다.
- 동일 타입끼리는 일반적으로 “더 구체적인 규칙”이 우선된다(이번 예제에서 Prefix의 longest‑match, 정규식의 조건 일치 등).
- 테스트 패턴대로 실제 요청으로 파드명까지 확인하면, 매칭 규칙을 문서가 아닌 “런타임 사실”로 검증할 수 있다.
인그레스 TLS Termination
👍 Cilium Ingress Example with TLS Termination :
➡️ Cilium Ingress Controller가 L7 Load Balancer 역할을 하면서 HTTPS(TLS) 연결을 직접 종료(Terminate)하는 방법을 보여주는 예제입니다.
🔹 TLS Termination이란?
- 클라이언트(브라우저/앱) ↔ Ingress Controller 구간은 HTTPS로 통신
- Ingress Controller(Cilium)가 인증서/키를 가지고 있어서 TLS 세션을 종료(복호화)
- 이후 백엔드 서비스(Pod)로는 평문 HTTP로 전달
즉, 외부 트래픽은 암호화 보안 유지, 내부 트래픽은 단순 HTTP로 효율성 확보합니다.
🔹 의미 / 시사점
- 보안: 외부와의 트래픽은 TLS 보호
- 단순화: 백엔드는 TLS 몰라도 됨
- 유연성: 도메인별 인증서 여러 개 지정 가능 → 멀티호스트 지원
- 관리: Let’s Encrypt, cert-manager 같은 도구와 연동해서 Secret 자동 관리 가능
# For demonstration purposes we will use a TLS certificate signed by a made-up, self-signed certificate authority (CA).
# One easy way to do this is with mkcert. We want a certificate that will validate bookinfo.cilium.rocks and hipstershop.cilium.rocks, as these are the host names used in this example.
apt install mkcert -y
mkcert -h
#
mkcert '*.cilium.rocks'
#
ls -l *.pem
-rw------- 1 root root 1708 Aug 17 12:11 _wildcard.cilium.rocks-key.pem
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1452 Aug 17 12:11 _wildcard.cilium.rocks.pem
#
openssl x509 -in _wildcard.cilium.rocks.pem -text -noout
Issuer: O = mkcert development CA, OU = root@k8s-ctr, CN = mkcert root@k8s-ctr
Validity
Not Before: Aug 17 03:11:30 2025 GMT
Not After : Nov 17 03:11:30 2027 GMT
Subject: O = mkcert development certificate, OU = root@k8s-ctr
...
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Key Usage: critical
Digital Signature, Key Encipherment
X509v3 Extended Key Usage:
TLS Web Server Authentication
X509v3 Authority Key Identifier:
7E:20:AF:5F:00:4A:C8:6B:D6:44:C5:4F:32:C0:ED:FB:3C:0D:30:00
X509v3 Subject Alternative Name:
DNS:*.cilium.rocks
openssl rsa -in _wildcard.cilium.rocks-key.pem -text -noout
Private-Key: (2048 bit, 2 primes)
modulus:
00:cb:35:d6:f0:e2:77:41:4b:ea:39:ea:06:bc:5d:
...
# Mkcert created a key (_wildcard.cilium.rocks-key.pem) and a certificate (_wildcard.cilium.rocks.pem) that we will use for the Gateway service.
# Create a Kubernetes TLS secret with this key and certificate:
kubectl create secret tls demo-cert --key=_wildcard.cilium.rocks-key.pem --cert=_wildcard.cilium.rocks.pem
kubectl get secret demo-cert -o json | jq
🔹 1. TLS Termination 실습을 위한 인증서 준비
- mkcert '*.cilium.rocks' 로 생성한 인증서는 와일드카드 도메인 인증서 → bookinfo.cilium.rocks, hipstershop.cilium.rocks 등 여러 서비스에 재사용 가능
- openssl 명령으로 발급 주체(issuer), 유효기간, Subject Alternative Name(SAN) 등 인증서 메타데이터를 확인하여 TLS 서버 인증에 적합한지 검증
👉 시사점: 운영 환경에서도 마찬가지로, Ingress에서 TLS 종료를 하려면 올바른 인증서와 키가 필요하며, SAN 필드가 서비스 도메인을 반드시 커버해야 한다는 것을 강조합니다.
.
🔹 2. Kubernetes Secret으로 관리
- 생성한 PEM 파일을 kubectl create secret tls demo-cert ... 로 Secret에 저장
- Ingress 리소스에서 spec.tls.secretName: demo-cert 로 참조하여 TLS 종료에 활용
👉 시사점: 쿠버네티스에서 TLS 키/인증서는 개별 Pod에 배포하지 않고 Secret 리소스로 중앙 관리 → 보안 및 운영 일관성 확보.
🔹 3. 자체 서명 인증서(Self-signed)로도 기능 검증 가능
- mkcert는 신뢰할 수 있는 CA가 아니므로 브라우저/클라이언트에서 경고가 발생하지만, 테스트 환경에서는 Ingress TLS termination 동작 자체를 검증할 수 있음.
- 실제 운영에서는 Let's Encrypt(cert-manager 연동)나 상용 CA 인증서를 사용해야 함.
👉 시사점:
- 테스트/POC 단계에서는 mkcert 같은 self-signed 인증서를 써서 기능 검증
- 운영 환경에서는 자동화(cert-manager, ACME) + 신뢰할 수 있는 CA 인증서 필요
🔹 4. 보안 & 아키텍처적 의미
- Ingress Controller(Cilium)가 TLS 세션을 직접 종료하므로,
- 백엔드 Pod는 평문 HTTP만 처리 → 단순화 및 성능 향상
- 외부와의 트래픽은 여전히 TLS로 보호 → 보안 요구사항 충족
- 하나의 와일드카드 인증서를 여러 서비스 도메인에 적용 가능 → 멀티 서비스 운영에 효율적
✅ 정리
이 테스트는
- (1) Ingress의 TLS termination 기능 검증을 위한 자체 서명 인증서 생성/활용 과정,
- (2) Kubernetes에서 인증서를 Secret으로 관리하고 Ingress에 연결하는 패턴,
- (3) 운영 환경에서는 자동 인증서 관리(cert-manager) 필요성을 시사합니다.
GATEWAY API
👍 Kubernetes 진영에서 최근 활발하게 논의되는 Gateway API는 기존 Ingress를 확장·대체하려는 차세대 서비스 네트워킹 API 표준입니다.
🔹 Gateway API란?
- Kubernetes SIG-NETWORK에서 개발 중인 서비스 네트워킹 CRD 세트
- Ingress의 한계를 보완하고, L4/L7 네트워킹(HTTP, TCP, TLS, gRPC 등)을 더 유연하고 일관성 있게 정의할 수 있도록 설계됨
- "Ingress v2" 라고 불리기도 하지만, 단순 교체가 아니라 더 범용적인 네트워킹 API
🔹 기존 Ingress의 한계
- 오직 HTTP(S) L7 트래픽만 정의 가능 (TCP/UDP 지원 부족)
- Controller별 annotation 의존도가 커서 이식성 낮음
- 하나의 Ingress 리소스에 너무 많은 설정을 몰아넣음 → 역할 분리가 어려움
🔹 Gateway API의 주요 리소스
Gateway API는 여러 CRD(Custom Resource Definition)로 나뉘며, 역할을 분리합니다.
- GatewayClass
- 클러스터 전역에서 사용 가능한 “게이트웨이 구현체” 정의
- 예: Cilium Gateway, NGINX Gateway, Istio Gateway
- Gateway
- 실제 데이터 평면에서 Load Balancer / Proxy 인스턴스를 표현
- IP/호스트/포트 바인딩 정보 포함
- Routes
- 트래픽 라우팅 규칙 정의
- 타입별로 존재:
- HTTPRoute (HTTP, gRPC)
- TLSRoute
- TCPRoute
- UDPRoute
- GRPCRoute (실험적)
- Policy
- 보안, 인증, QoS 같은 정책을 독립적으로 붙일 수 있음
👉 Ingress는 단일 오브젝트였지만, Gateway API는 구성요소를 나눠서 역할별 책임을 분리
Gateway API의 핵심 특징
🚀 Kubernetes Gateway API의 핵심 특징
Kubernetes에서 서비스 네트워킹을 다루는 새로운 표준인 Gateway API는 기존 Ingress의 한계를 보완하면서 더 강력하고 유연한 기능을 제공합니다.
특히 멀티 프로토콜 지원과 역할 기반의 리소스 모델은 앞으로 Kubernetes 네트워킹의 중심이 될 가능성이 큽니다.
🔑 Gateway API의 주요 특징
1. 개선된 리소스 모델
Gateway API는 GatewayClass, Gateway, Route(HTTPRoute, TCPRoute 등)와 같은 새로운 리소스를 도입했습니다.
이를 통해 라우팅 규칙을 더 세밀하고 직관적으로 정의할 수 있습니다.
2. 프로토콜 독립적
Ingress가 주로 HTTP(S)만 지원했던 것과 달리, Gateway API는 TCP, UDP, TLS, gRPC까지 포괄적으로 지원합니다.
즉, L4~L7 전반의 트래픽을 유연하게 처리할 수 있습니다.
3. 강화된 보안
TLS 구성과 세밀한 접근 제어 기능이 기본 내장되어 있습니다.
이는 보안 정책을 더 명확하게 정의하고 서비스별로 적용할 수 있다는 장점이 있습니다.
4. 교차 네임스페이스 지원
다른 네임스페이스의 서비스로도 트래픽을 라우팅할 수 있어,
더 유연하고 모듈화된 아키텍처를 설계할 수 있습니다.
5. 확장성
Gateway API는 정책 리소스나 사용자 정의 확장을 쉽게 붙일 수 있도록 설계되었습니다.
이를 통해 조직의 요구사항에 맞춘 맞춤형 네트워킹을 구현할 수 있습니다.
6. 역할 지향적 설계 (가장 흥미로운 부분 ✨)
운영자, 애플리케이션 개발자, 보안 팀 간의 역할과 책임을 명확하게 분리합니다.
예를 들어, 운영자는 Gateway를 관리하고, 개발자는 Route를 정의하며, 보안팀은 정책을 적용하는 식입니다.
이로써 팀 간 충돌을 줄이고 협업 효율을 높이는 구조가 가능해집니다.
✅ 정리
Gateway API는 단순히 Ingress의 대체제가 아니라, Kubernetes 네트워킹의 차세대 표준으로 자리잡을 준비를 하고 있습니다.
멀티 프로토콜 지원, 보안 강화, 역할 기반 설계는 클라우드 네이티브 환경에서 필수적인 요구사항을 충족시켜 주며,
앞으로의 Kubernetes 네트워크 아키텍처에 큰 변화를 가져올 것으로 기대됩니다.

인그레스의 제약
- Ingress 제약 : 고급 라우팅 지원 부족(URL rewriting 등), TCP/UDP 등 프로토콜 지원 부족, 세부 권한 분리 부족

- 사전준비
- Cilium must be configured with NodePort enabled, using nodePort.enabled=true or by enabling the kube-proxy replacement with kubeProxyReplacement=true. For more information, see kube-proxy replacement.
- Cilium must be configured with the L7 proxy enabled using l7Proxy=true (enabled by default).
- The below CRDs from Gateway API v1.2.0 must be pre-installed. Please refer to this docs for installation steps. Alternatively, the below snippet could be used. → CRD 설치 필수!
# CRD 설치
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.2.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_gatewayclasses.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.2.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_gateways.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.2.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_httproutes.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.2.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_referencegrants.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.2.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_grpcroutes.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.2.0/config/crd/experimental/gateway.networking.k8s.io_tlsroutes.yaml
# 확인
kubectl get crd | grep gateway.networking.k8s.io
gatewayclasses.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2025-08-17T04:27:28Z
gateways.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2025-08-17T04:27:28Z
grpcroutes.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2025-08-17T04:27:30Z
httproutes.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2025-08-17T04:27:29Z
referencegrants.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2025-08-17T04:27:29Z
tlsroutes.gateway.networking.k8s.io 2025-08-17T04:27:30Z1. GATEWAY API 배포
#
helm upgrade cilium cilium/cilium --version 1.18.1 --namespace kube-system --reuse-values \
--set ingressController.enabled=false --set gatewayAPI.enabled=true
#
kubectl -n kube-system rollout restart deployment/cilium-operator
kubectl -n kube-system rollout restart ds/cilium
#
cilium config view | grep gateway-api
enable-gateway-api true
enable-gateway-api-alpn false
enable-gateway-api-app-protocol false
enable-gateway-api-proxy-protocol false
enable-gateway-api-secrets-sync true
gateway-api-hostnetwork-enabled false
gateway-api-hostnetwork-nodelabelselector
gateway-api-secrets-namespace cilium-secrets
gateway-api-service-externaltrafficpolicy Cluster
gateway-api-xff-num-trusted-hops 0
# cilium-ingress 제거 확인
kubectl get svc,pod -n kube-system
# The GatewayClass is a type of Gateway that can be deployed: in other words, it is a template. This is done in a way to let infrastructure providers offer different types of Gateways. Users can then choose the Gateway they like.
# For instance, an infrastructure provider may create two GatewayClasses named internet and private to reflect Gateways that define Internet-facing vs private, internal applications.
# In our case, the Cilium Gateway API (io.cilium/gateway-controller) will be instantiated.
# This schema below represents the various components used by Gateway APIs. When using Ingress, all the functionalities were defined in one API. By deconstructing the ingress routing requirements into multiple APIs, users benefit from a more generic, flexible and role-oriented model
# The actual L7 traffic rules are defined in the HTTPRoute API.
# In the next challenge, you will deploy an application and set up GatewayAPI HTTPRoutes to route HTTP traffic into the cluster.
kubectl get GatewayClass
NAME CONTROLLER ACCEPTED AGE
cilium io.cilium/gateway-controller True 2m19s
kubectl get gateway -A
No resources found2. 게이트웨이, HTTPROUTE 배포
#
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: my-gateway
spec:
gatewayClassName: cilium
listeners:
- protocol: HTTP
port: 80
name: web-gw
allowedRoutes:
namespaces:
from: Same
---
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: http-app-1
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
namespace: default
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /details
backendRefs:
- name: details
port: 9080
- matches:
- headers:
- type: Exact
name: magic
value: foo
queryParams:
- type: Exact
name: great
value: example
path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /
method: GET
backendRefs:
- name: productpage
port: 9080
EOF
# You will see a LoadBalancer service named cilium-gateway-my-gateway which was created for the Gateway API.
kubectl get svc,ep cilium-gateway-my-gateway
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/cilium-gateway-my-gateway LoadBalancer 10.96.240.104 192.168.10.211 80:31017/TCP 96s
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
endpoints/cilium-gateway-my-gateway 192.192.192.192:9999 96s
# The same external IP address is also associated to the Gateway:
kubectl get gateway
NAME CLASS ADDRESS PROGRAMMED AGE
my-gateway cilium 192.168.10.211 True 14s
## Accepted: the Gateway configuration was accepted.
## Programmed: the Gateway configuration was programmed into Envoy.
## ResolvedRefs: all referenced secrets were found and have permission for use.
kc describe gateway
#
kubectl get httproutes -A
NAMESPACE NAME HOSTNAMES AGE
default http-app-1 8m12s
# Accepted: The HTTPRoute configuration was correct and accepted.
# ResolvedRefs: The referenced services were found and are valid references.
kc describe httproutes
# Check Cilium Operator logs
kubectl logs -n kube-system deployments/cilium-operator | grep gateway
- 게이트웨이 외부 주소 확인
- Gateway 리소스가 LoadBalancer IP를 할당받았는지 확인하고, 이를 통해 외부 접근이 가능함을 보여줍니다.
- 경로 기반 매칭(Path Matching)
- /details/1 요청을 보내면 HTTPRoute 규칙에 따라 details 서비스(9080 포트)로 정확히 전달되는 것을 확인합니다.
- 외부 네트워크 접근성 확인
- 클러스터 외부 호스트(router)에서 동일한 요청을 보내, 게이트웨이가 외부에서도 접근 가능한 엔드포인트임을 검증합니다.
- 헤더·쿼리 기반 매칭(Header/Query Matching)
- magic: foo 헤더와 ?great=example 쿼리를 포함한 요청이 규칙에 맞춰 지정된 백엔드로 라우팅되는 것을 확인합니다.
👉 정리하면, 이 테스트는 Gateway API가 단순히 경로 기반 라우팅만 지원하는 것이 아니라, HTTP 헤더나 쿼리 같은 세밀한 L7 조건까지 활용해 트래픽을 유연하게 분기할 수 있음
#
GATEWAY=$(kubectl get gateway my-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.addresses[0].value}')
echo $GATEWAY
# HTTP Path matching
# Let's now check that traffic based on the URL path is proxied by the Gateway API.
# Check that you can make HTTP requests to that external address:
# Because the path starts with /details, this traffic will match the first rule and will be proxied to the details Service over port 9080.
curl --fail -s http://"$GATEWAY"/details/1 | jq
sshpass -p 'vagrant' ssh vagrant@router "curl -s --fail -v http://"$GATEWAY"/details/1"
# HTTP Header Matching
# This time, we will route traffic based on HTTP parameters like header values, method and query parameters. Run the following command:
curl -v -H 'magic: foo' http://"$GATEWAY"\?great\=example
sshpass -p 'vagrant' ssh vagrant@router "curl -s -v -H 'magic: foo' http://"$GATEWAY"\?great\=example"
- Gateway 리소스 생성 (tls-gateway)
- gatewayClassName: cilium 사용
- 두 개의 HTTPS Listener 정의 (포트 443 공통)
- bookinfo.cilium.rocks → demo-cert 인증서
- webpod.cilium.rocks → demo-cert 인증서
- 즉, 하나의 Gateway에서 여러 호스트네임을 동시에 처리 (SNI 기반 다중 TLS).
- HTTPRoute 리소스 생성
- https-app-route-1
- Host: bookinfo.cilium.rocks
- PathPrefix /details → details 서비스(9080 포트)
- https-app-route-2
- Host: webpod.cilium.rocks
- PathPrefix / → webpod 서비스(80 포트)
- https-app-route-1
상태 확인
kubectl get gateway tls-gateway
kubectl get httproutes https-app-route-1 https-app-route-2
-
- Gateway 주소(192.168.10.213) 할당 확인
- 두 HTTPRoute 모두 원하는 호스트네임과 연결됨을 확인
- TLS 접속 테스트 (curl --resolve 사용)
- /etc/hosts를 수정하지 않고, curl에서 직접 DNS 매핑 지정
- bookinfo.cilium.rocks 요청 시: HTTPS + Path /details/1 → details 서비스로 라우팅
- webpod.cilium.rocks 요청 시: HTTPS + Path / → webpod 서비스로 라우팅
#
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: tls-gateway
spec:
gatewayClassName: cilium
listeners:
- name: https-1
protocol: HTTPS
port: 443
hostname: "bookinfo.cilium.rocks"
tls:
certificateRefs:
- kind: Secret
name: demo-cert
- name: https-2
protocol: HTTPS
port: 443
hostname: "webpod.cilium.rocks"
tls:
certificateRefs:
- kind: Secret
name: demo-cert
---
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: https-app-route-1
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: tls-gateway
hostnames:
- "bookinfo.cilium.rocks"
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /details
backendRefs:
- name: details
port: 9080
---
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: https-app-route-2
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: tls-gateway
hostnames:
- "webpod.cilium.rocks"
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /
backendRefs:
- name: webpod
port: 80
EOF
#
kubectl get gateway tls-gateway
NAME CLASS ADDRESS PROGRAMMED AGE
tls-gateway cilium 192.168.10.213 True 9m25s
kubectl get httproutes https-app-route-1 https-app-route-2
NAME HOSTNAMES AGE
https-app-route-1 ["bookinfo.cilium.rocks"] 9m43s
https-app-route-2 ["webpod.cilium.rocks"] 9m43s
#
GATEWAY2=$(kubectl get gateway tls-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.addresses[0].value}')
echo $GATEWAY2
curl -s --resolve bookinfo.cilium.rocks:443:${GATEWAY2} https://bookinfo.cilium.rocks/details/1 | jq
curl -s --resolve webpod.cilium.rocks:443:${GATEWAY2} https://webpod.cilium.rocks/ -v
TLS Route ( Terminate vs Passthrough )
Gateway API의 TLSRoute에서 중요한 개념이 바로 Terminate 모드와 Passthrough 모드입니다. 두 모드의 차이는 “게이트웨이가 TLS 연결을 어디서 끊느냐(종료하느냐)”에 있습니다.
- In Terminate:
- Client → Gateway: HTTPS
- Gateway → Pod: HTTP
- In Passthrough:
- Client → Gateway: HTTPS
- Gateway → Pod: HTTPS
🔹 1. Terminate 모드 (TLS Termination)
- 게이트웨이가 TLS 세션을 종료
- 클라이언트 ↔ 게이트웨이 구간은 HTTPS(암호화)
- 게이트웨이 ↔ 백엔드 서비스 구간은 평문 HTTP (혹은 다시 내부 TLS를 붙일 수도 있지만 일반적으로 평문)
- 게이트웨이가 Secret(인증서/키)을 참조하여 TLS 핸드셰이크를 직접 처리
👉 특징
- 게이트웨이가 트래픽 내용을 복호화하므로, L7 라우팅(HTTP Path/Host 기반 분기) 가능
- 보안 인증 관리(인증서) 책임이 게이트웨이에 있음
- 가장 일반적인 HTTPS Ingress 패턴
🔹 2. Passthrough 모드 (TLS Passthrough)
- 게이트웨이는 TLS 세션을 종료하지 않음
- 클라이언트 ↔ 백엔드 서비스 구간이 end-to-end TLS (게이트웨이는 단순 프록시)
- 게이트웨이는 SNI(Server Name Indication) 필드만 읽어서 백엔드 선택
- 백엔드 서비스가 직접 TLS 인증서를 가지고 세션 종료
👉 특징
- 게이트웨이는 암호화된 페이로드를 해독하지 않음 → 보안 경계가 백엔드 서비스로 이동
- L4 수준 라우팅만 가능 (Host/SNI 기반 분기 가능, HTTP Path나 Header 기반 매칭은 불가)
- 각 백엔드 서비스별로 TLS 인증서 관리 필요
1. deploy app
# Deploy the Demo app : HTTPS 웹서버
# We will be using a NGINX web server. Review the NGINX configuration.
cat <<'EOF' > nginx.conf
events {
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] $status '
'"$request" $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
server {
listen 443 ssl;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html;
server_name nginx.cilium.rocks;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx-server-certs/tls.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx-server-certs/tls.key;
}
}
EOF
# As you can see, it listens on port 443 for SSL traffic. Notice it specifies the certificate and key previously created.
# We will need to mount the files to the right path (/etc/nginx-server-certs) when we deploy the server.
# The NGINX server configuration is held in a Kubernetes ConfigMap. Let's create it.
kubectl create configmap nginx-configmap --from-file=nginx.conf=./nginx.conf
# Review the NGINX server Deployment and the Service fronting it:
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-nginx
labels:
run: my-nginx
spec:
ports:
- port: 443
protocol: TCP
selector:
run: my-nginx
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-nginx
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
run: my-nginx
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
run: my-nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: my-nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 443
volumeMounts:
- name: nginx-config
mountPath: /etc/nginx
readOnly: true
- name: nginx-server-certs
mountPath: /etc/nginx-server-certs
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: nginx-config
configMap:
name: nginx-configmap
- name: nginx-server-certs
secret:
secretName: demo-cert
EOF
# Verify the Service and Deployment have been deployed successfully:
kubectl get deployment,svc,ep my-nginx
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/my-nginx 1/1 1 1 48s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/my-nginx ClusterIP 10.96.142.252 <none> 443/TCP 48s
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
endpoints/my-nginx 172.20.1.59:443 48s2. deploy Gateway
#
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: cilium-tls-gateway
spec:
gatewayClassName: cilium
listeners:
- name: https
hostname: "nginx.cilium.rocks"
port: 443
protocol: TLS
tls:
mode: Passthrough
allowedRoutes:
namespaces:
from: All
---
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1alpha2
kind: TLSRoute
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: cilium-tls-gateway
hostnames:
- "nginx.cilium.rocks"
rules:
- backendRefs:
- name: my-nginx
port: 443
EOF
# The Gateway does not actually inspect the traffic aside from using the SNI header for routing. Indeed the hostnames field defines a set of SNI names that should match against the SNI attribute of TLS ClientHello message in TLS handshake.
# Let's now deploy the Gateway and the TLSRoute to the cluste
kubectl get gateway cilium-tls-gateway
NAME CLASS ADDRESS PROGRAMMED AGE
cilium-tls-gateway cilium 172.18.255.202 True 8s
GATEWAY=$(kubectl get gateway cilium-tls-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.addresses[0].value}')
echo $GATEWAY
# Let's also double check the TLSRoute has been provisioned successfully and has been attached to the Gateway.
kubectl get tlsroutes.gateway.networking.k8s.io -o json | jq '.items[0].status.parents[0]'
...
3. Make TLS requests
# The data should be properly retrieved, using HTTPS (and thus, the TLS handshake was properly achieved).
# There are several things to note in the output.
## It should be successful (you should see at the end, a HTML output with Cilium rocks.).
## The connection was established over port 443 - you should see Connected to nginx.cilium.rocks (172.18.255.200) port 443 .
## You should see TLS handshake and TLS version negotiation. Expect the negotiations to have resulted in TLSv1.3 being used.
## Expect to see a successful certificate verification (look out for SSL certificate verify ok).
curl -v --resolve "nginx.cilium.rocks:443:$GATEWAY" "https://nginx.cilium.rocks:443"
# (추가) nginx 파드 내에서 tcpudmp 나 access log 확인해보기!'컨테이너 > 쿠버네티스 네트워크' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Cilium] (18) 실리움 네트워킹 _ Cilium Security (2) | 2025.09.02 |
|---|---|
| [Cilium] (16) 실리움 네트워킹 _ k8s performance test (0) | 2025.08.29 |
| [Cilium] (14) 실리움 네트워킹 _ Service LB IPAM (BGP) (1) | 2025.08.12 |
| [Cilium] (13) 실리움 네트워킹 _ BGP Control Plane (8) | 2025.08.12 |
| [Cilium] (12) 실리움 네트워킹 _ Service LB-IPAM (4) | 2025.08.06 |



